It’s inevitable that you’ll have to fix a 404-page error on your WordPress website at one point or another. Everything from plugin incompatibilities to changing slugs can affect how people view your content.
When starting your website or blog with WordPress, people sometimes offer unsolicited advice on how best to do this.
Some advice includes using sites where you’re given snippets of code, which you put on your website. They often work like magic, bringing up pop-ups and many other cool features. Often, it becomes spammy. And even after deleting them, the site might still break!
This could send you into panic mode, where you’re worried about your content, the sales you’re not making, and more. The truth is, 404s are not as infrequent as you think they are; everyone has them!
It can happen at least one or more times.
It’s the last thing you want visitors and clients to see on your website, and it can be quite distressing for a beginner. Let’s talk a bit further about 404’s.
What does ‘Error 404’ Not Found Mean?
Error 404 means that the user cannot find specific content on a website. Even though the user successfully connected to the website’s server, it couldn’t find the file requested because there was no resource at that URL.
For instance, if a user tries to access a URL from your page that doesn’t exist, he or she will get a 404 error page because the request isn’t available. This could happen even if you changed or hidden the URL from view to edit the content.
Or, perhaps you publish a post with a long URL, which you later shortened.
Any time the old URL is used, a 404 page comes up. This does not happen to only blog posts. Pages, images, videos, CSS, or JavaScript that are missing can also be affected.
How Does the 404 Error Occur?
HTTP status codes are used to communicate with your website users. Your website’s server normally returns the appropriate HTTP status code when a visitor attempts to load a web page.
There are dozens of different HTTP status codes, each of which is used in different situations. So, In this case, if the requested web page is available, the visitor’s web browser will receive a 200 HTTP status code from your website server.
But if the requested web page is not available, a 404 HTTP status code is generated.
What Causes Error 404 Not Found on WordPress?
A 404 error isn’t the worst. Everyone gets them at one time or the other. They only become concerning when they interfere with your website’s functionality. This error can occur due to the site owner’s actions or that of the users.
As a Site Owner:
- Content hasn’t been uploaded to the page.
- Migration from one domain name to another without changing links.
- Plugin incompatibility that causes URLs to break.
- Deleting or hiding content after it has been published.
- Uninstalling a plugin that was controlling URLs for content.
As a Site Visitor
- URL was entered or copied incorrectly.
- The link to the address is faulty.
Variations of Error 404 Messages from WordPress and Other Sites
Various browsers give error messages differently. On Google Chrome, what you see is: “404. That’s an error. The requested URL was not found on this server. That’s all we know.”
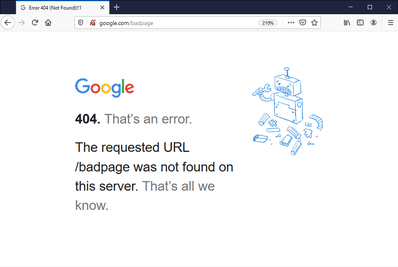
Other messages from various platforms are similar. They can include:
- Not found
- Error 404
- 404 Not Found
- This page cannot be found
- We can’t find the page you’re looking for
- HTTP Error 404
- The requested URL was not found on this server
Other times, these disappointing messages are overshadowed by the creativity applied to customized 404 pages.
For example:

Site owners can choose to be proactive by customizing their own 404 error page in WordPress. This is what shows up instead of the browser’s alternative, which allows the site owner to give more information.
Some may opt to redirect the user to the actual page. Though, this is often done when the developer changed the URL on purpose and creates a 301 redirect.
What Effects Does a 404 Error Have On Your WordPress Website?
Page not found 404 errors can exert influence on SEO. These types of errors are bad for SEO as search engines do not like to see websites with this particular problem.
Unchecked, 404s prevent search engine crawlers from your website’s content. This is because crawlers often follow internal links across your website. With a 404 error page, search engines assume the page is void of content.
This also causes the website to lose equity, thus limiting search engine optimization.
Visitors who follow a link on another website that connects to a page on your site with the wrong URL will also receive the 404-error message. This can lead you to lose traffic to your website. As a result, it will not generate link equity to rank higher in search.
More importantly, visitors are negatively affected by 404 errors. When people visit your site, they expect it to bring up the right page when they click on a link. The 404 error prevents visitors from accessing the desired WordPress webpages.
When the 404s become too frequent, visitors will leave the site and may never come back. This robs you of the chance to turn visitors into customers.
Fixing Error 404 On WordPress
Dealing with 404’s can be very rewarding. It may be taxing, trying to figure out the source of the problem. But you’ll be pleased to have your site running as it should without freak glitches.
Before we go on, there is one very important thing that must be done before you attempt to fix 404 problems. Back up your files!
You don’t want to forget to do this before making changes to your site. In the event something goes wrong, you’ll be able to recover without losing your content.
Now, we’ll go on to practical ways of fixing your error 404 pages.
Update Your Permalinks
Fixing URLS involves doing so manually by going to your permalinks in settings and saving changes. It is more applicable with error 404 messages seen after migrating from one domain to another.
You need to go to your permalinks in the settings section, select the preferred option and save changes. This solves some of the problems caused within WordPress.
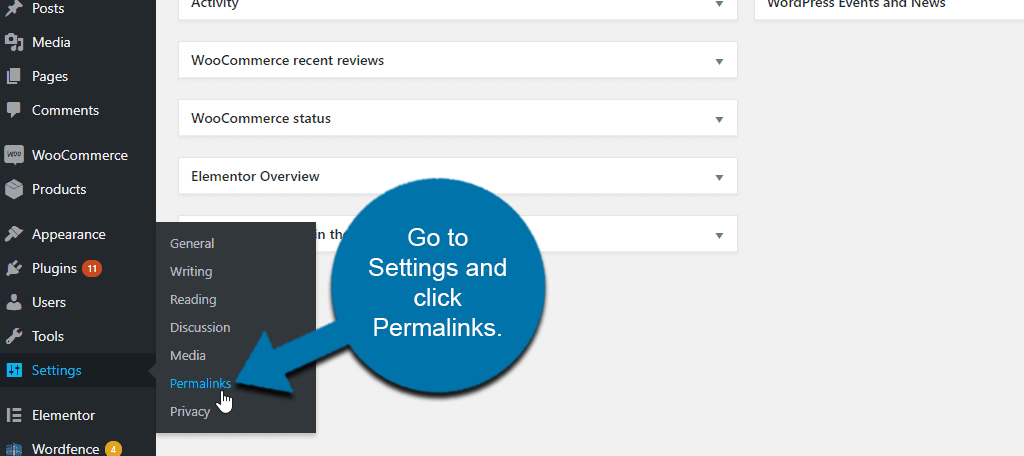
In fact, sometimes simply clicking “Save Changes” without changing anything forces WordPress to reinitialize the permalinks. It actually solves a lot of URL-related issues and is the first thing many developers will check.
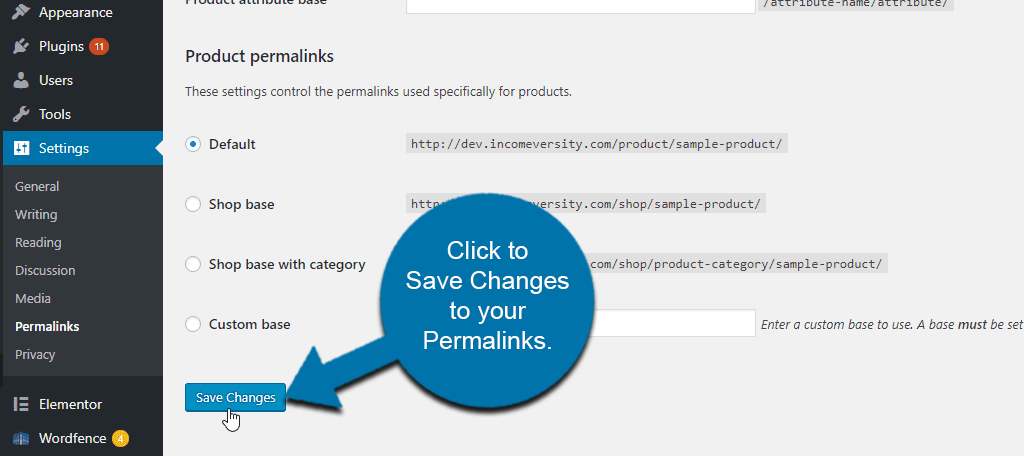
Adjusting permalinks is usually recommended as the first step before trying the plugins. If you still get the same error for some pages, they might be cached by your browser. You may need to clear your browser cache before changes are visible.
Using Plugins
This is when you set up 301 redirects for content that have been renamed, moved, or deleted. Sometimes 404s show up because the URL for content has been changed, or the resources on the page have been edited, deleted, or moved somewhere else manually.
Thus, visitors try to go to the old location or use the old URL. Automatically redirecting them to the new page if it exists is often the best fix.
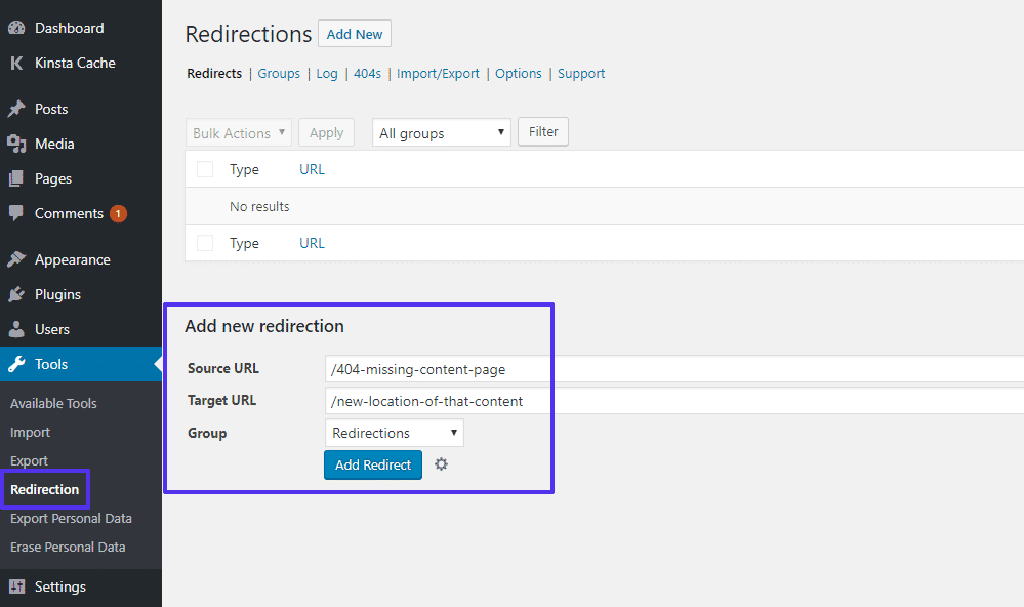
For the plugins, you navigate to your dashboard and then to plugins. Input 404 in the keyword search. Some of these plugins include Redirection, 404 to 301, 404-Page your smart custom 404 error page, and more.
The Redirection plugin has been around for a while, and it’s still getting updates, making it a very good fit for your website.
Click on install and activate for a specific plugin such as ‘404 redirect to homepage’. It is enabled by default and then appears in your menu. The 404 URL will then show a list of all the links or incoming traffic to your non-existent pages.
This way, you can track it and see how many hits specific pages get.
These plugins will detect 404s, and when they happen, redirect every one of your 404 pages to a page you specify, usually your homepage. Any other page or post can also be used, which keeps your visitors engaged and saves you from losing them.
They can also notify you that there is a 404 in the first place. You then decide the page to redirect visitors to, preferably a page that’s better suited for that particular 404.
These plugins would redirect a 404 as soon as it is detected and before Google finds it. Otherwise, a Google bot may land on a 404 first which could hurt your SERPs.
Using Google Search Console
You may also find 404’s in Google’s Search Console. You can go through your 404’s here and fix them by redirecting them; sometimes, it was a page you failed to create.
Sometimes, the reason for the error is a difference in the domain name of the page that should be on the site and what is currently available. This may be due to a change in the website.
Fixing this case doesn’t necessarily require an extra plugin. You can use the ‘.htaccess’ if your host uses an Apache server.
These steps can help fix a 404 issue. However, you can reach out to WordPress Support Service for assistance if it persists. One of WordPress’ many developers may help you out.
Another thing you can do is create your own 404 page and customize it to help your guests find their way back to your website. Plugins are also useful here. An example of this is the 404-Page plugin, for instance.
Creating Your Own Error 404 Not Found Page on WordPress
Although we have discussed extensively fixing your 404 pages, sometimes, they will still happen for a variety of reasons. You want to be prepared.
You can do much on your end to avoid 404s, but user factors are not within your reach. A user might input a wrong URL, and a 404 page comes up.
The standard 404-page WordPress contains a short message saying the page is missing under the search bar. Customizing your page gives you something better to display.
First, we install a free plugin to help it set up. Something like the 404page plugin is a good tool to install and activate. Other plugins are 404page or Custom 404 Pro.
Next, we create a new page to serve as the custom 404 page. Then, we go ahead and add any content we want. The content can include:
- adding an image
- a message explaining that the page is missing
- a list of main pages and post categories
- the most popular blog posts
- perhaps a button to bring the reader back to the home page
Afterward, you can publish the custom 404 page, which will have a chance to further engage the visitor.
Go to appearance and click the 404 error page. Here, we choose the new 404 page from the dropdown menu.
We save the changes and test the 404 page to ensure it is live and active on the site. If anyone visits a deleted page or an incorrect URL on the site, they will be redirected to this new 404 page instead of the original.
Having a customized error 404 page like this will be much better for keeping people on the site and help improve rating with Google by lowering bounce rates. It is very important, though, to keep the customized page light.
How Do You Monitor 404 Errors in the Future?
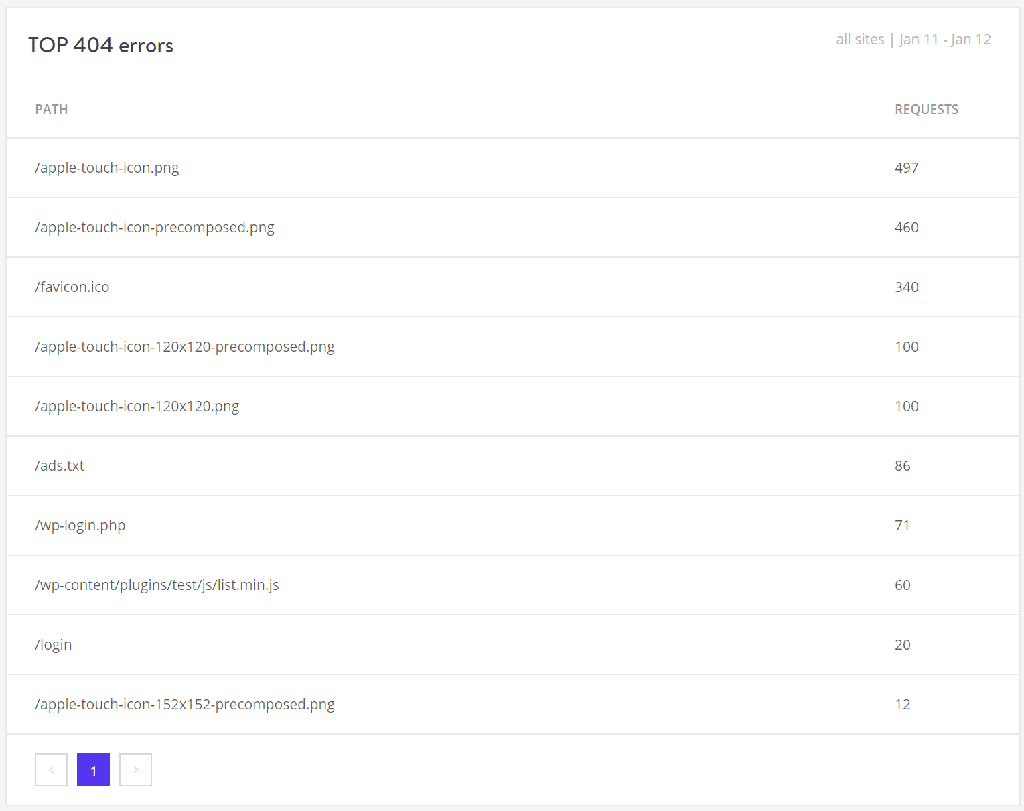
Pay close attention to pages and posts generating 404 errors by using any of the tools below.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console allows you to track 404 issues that Google’s bot crawlers detect. It is the simplest and fastest method as it does not require any third-party plugins or further scanning of your sites.
Google bots constantly monitor your site, which helps to take advantage of that feature. Especially since it tracks hard and soft 404 errors.
Soft vs. Hard 404 Errors
There are two types of 404 errors found on WordPress: Soft and Hard. Hard 404 error occurs when the website’s server responds with a 404 HTTP status code.
A soft 404 error, on the other hand, is a faux error that occurs when your website delivers a 200 HTTP status code when Google believes it should return a 404 HTTP status code.
When Google scans a broken link on your website that leads to a non-existent web page, it logs the activity as a 404 error in Google Search Console. Access the coverage option in Search Console and click the excluded box in the upper right corner to see the 404 errors.
Hard and soft 404 will be present under the details section.
You must have added your WordPress site to Search Console to utilize this feature. You can do this by submitting the sitemap for your website. It is also an important step in SEO.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics tracks and displays 404 errors using custom reports. These are useful for tracking internal and external broken links that lead to bad pages on your site.
Internal links point from one page on your website to another. These errors can easily be fixed because you have full control over those links.
External links are those from other websites to pages or posts on your site. You don’t have direct control over these links and can’t just fix them. But it is still a problem with solutions that work.
Using a WordPress Plugin
Suppose you want to use a WordPress plugin. The Redirection plugin, as mentioned earlier, can do more than automatically redirect the pages. It can also let you monitor for 404 issues from your WordPress dashboard.
There’s a reason why this particular plugin is among the most popular and used tools in the WordPress repository. It works exceptionally well and helps you maintain your content.
Third-Party Audit Tool
The Internet has several third-party tools available for eliminating technical SEO issues and finding out how and where a website’s crawlability needs to be improved.
They analyze and give reports on the speed and performance of your website, how accessible your site is to bots and search engines, and can check the security of your WordPress installation.
You may also use a third-party audit tool like Ahrefs to check your WordPress site for 404 problems. You may even plan this to run regularly.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, 404 errors will occur on your site whether you like it or not. The bigger your WordPress site gets, the more visitors you’ll receive. I mean, that is the plan, after all.
We recommend creating a strong workflow for monitoring and correcting these types of issues and having a periodic schedule where you manually fix these problems. Automatic tools aren’t always the most reliable.
Keeping on top of your 404s helps your ratings as these errors are never good for your visitors, brand, or Google search results.
If this has helped you, or you have additional clarifications, kindly let us know in the comments below.



