According to a new report, data centers in China emitted 99 million metric tons of carbon dioxide in 2018. Data centers are the backbone of our always-online society and consume about 5% of global electricity.
This is beginning to rival the airline industry.
Data centers store electronic data including videos, photos, gaming servers, and web servers. Everything that connects to an online service or function is connecting to a data center.
This makes them an integral part of our society, but they are becoming a major carbon contributor.
How Can We Reduce Their Carbon Footprint
While the data centers themselves do not emit carbon dioxide, the energy sources that power them do. They run 24 hours a day, 7 days a week and produce a significant amount of heat.
Not only do you need to use electricity to power them, but a large amount of energy is consumed keeping them cool.
However, there is a solution.
Use renewable energy sources like solar and wind to power the data centers.
Why Renewable Energy Is Necessary
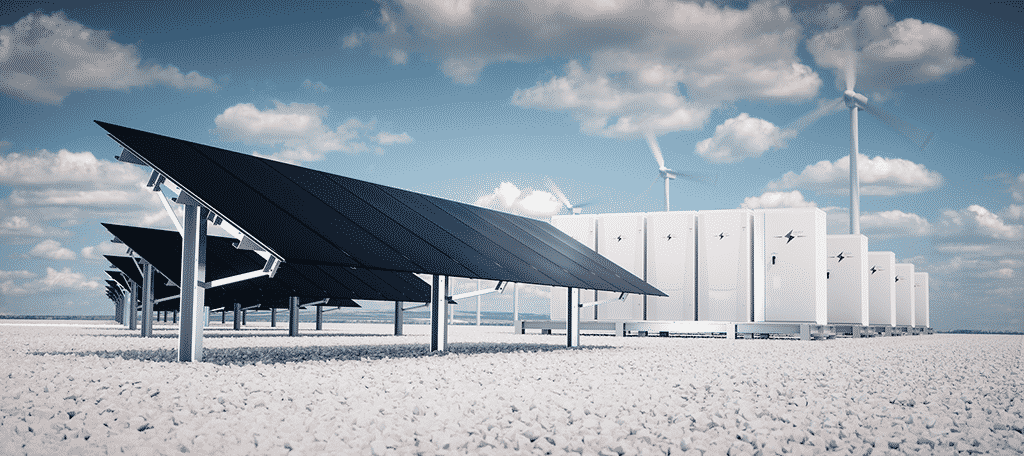
Our reliance on the internet is not going away anytime soon. In fact, it is expected to grow. The same report believes that the data centers in China will increase emissions from 99 to 163 million metric tons of carbon.
Since the usage will only increase, changing the power source is the only feasible answer. Luckily, China is already moving in this direction. It plans to increase renewable energy to 30% (currently 23%) by 2023.
This 7% jump will remove 16 million metric tons of carbon.
GreenGeeks Does This
As a green web hosting company, we take pride in the fact that our data centers give back three times the energy they use.
We carefully calculate the energy we use and purchase that amount three times over in wind energy to put back into the grid. This ensures that our servers are not adding carbon to the atmosphere. This means we have a net-negative carbon footprint.

