
The purpose of any website is to offer engaging content to attract an audience. But sometimes this material could be seen as a duplicated post; a copy of material that is also available elsewhere on the Internet. And some site owners will experience a drop in traffic from Google for duplicate content.
Pages that once had an incredible number of visitors could begin to lose their luster over time. However, some of these pages shortened lifespan could be the result of being identified as copied materials.
If this happens to you, does this mean Google is punishing you for duplicate content?
The short answer is: “No.” In reality, Google does not penalize for duplicate content. It’s in the way which Google displays results where some might think so.
It’s not like the worst types of penalties Google hands out for creating poor content. Duplicates are simply a victim of being ignored by the search engine.
What is Duplicate Content in SEO?
Experts believe that 30% of the content on the Internet is duplicated. This includes those who copy content on purpose as well as creating similar pieces of information.
Duplicate content is seen when two or more pages on the Internet have matching content.
And some believe you can receive a Google penalty for duplicate content on your website. In reality, this isn’t entirely the case.
Google is in the business of delivering the highest quality search results to users. This means it has to sift through content that is closely related and determine which is the most precise for the query.
Think of it more like confusing search engines regarding what content is the most prevalent. This often means the intended URL is surpassed by variations of its material.
Unfortunately, this means sometimes original content is buried while copies are displayed more prominently.
Some of the most common include:
- Canonical URL Issues
Canonical issues often arise when users will add both “http://yourwebsite.com” and “http://www.yourwebsite.com” throughout the site. - Not Using “Pretty” URLs
Using “pretty” URLs avoids a lot of linking issues while being more SEO friendly. For example, you can change the permalink structure of WordPress to be more open to users and Google. - Pagination of Comments
Comment pagination is when a webmaster will create “pages” for long comment threads. Sometimes the process will copy the original content on each page. - Using Printer-Friendly Content
Printer-friendly posts are often subject to duplication. This happens when both the original and the printer version are indexed by Google. - Page Tracking Additions
Tracking elements in URLs have the potential to create duplicate links because of the way they’re often structured. - Tags, Categories and Other CMS Elements
When using a content management system, some of its features can easily duplicate content. For example, a post in WordPress could be shown on the homepage in addition to the original post. - Content Scraping
Content scraping is when a site owner will copy the content from one page and put it onto his or her own. It borders on plagiarism and is frowned upon by many.
Now, this isn’t a complete list. But these are some of the most common ways content is duplicated in Google.
How Does Duplicate Content Affect Your Site?
Unfortunately, there is a myriad of ways duplicate content can be seen on the Internet. Which is probably why Google doesn’t out-right penalize web developers.
When copies of content are found in search, Google tries to retrieve the page that is most relevant to a user. This means things like syndicated content or curated websites have potential to rank higher than your own.
Although in many cases links to the original article are provided, it could still mean a loss of actual traffic to your own website.
If copies are found on your own website, this means you’ll essentially compete with yourself in search.
The end result may be that one page you don’t want could rank higher.
Easy Ways to Find Duplicate Content
Finding copies of your material is often a daunting task. This is especially true if you have an exceptional amount of content on your website.
However, it’s still a good idea to do what you can to find these copies and adjust your tactics. Even though you don’t get an official penalty from Google, you still want certain pages to rank.
Here are three ways I check for duplicate content. Perhaps one of them will work for you as well.
Searching through Google
That’s right, searching through Google manually is one of my go-to tasks. This is because Google has many ways to search which can provide some great results for a variety of purposes.
In this instance, you can search your site for specific lines of text whether in content or in title.
For example, you can use this term in Google to look for specific titles with exact keywords:
site:yoursite.com intitle:"keyword"
Of course, you want to change “yoursite.com” and “keyword” to your own search parameters.
If you’re searching for a specific line of text, use this in search:
site:yoursite.com "a specific line of text"
It’s the quotations around your keyword or phrases that tells Google to look for specific details in your content.
If you find more than one page with duplicate content, you know where you need to make changes.
Using SEO Review Tools
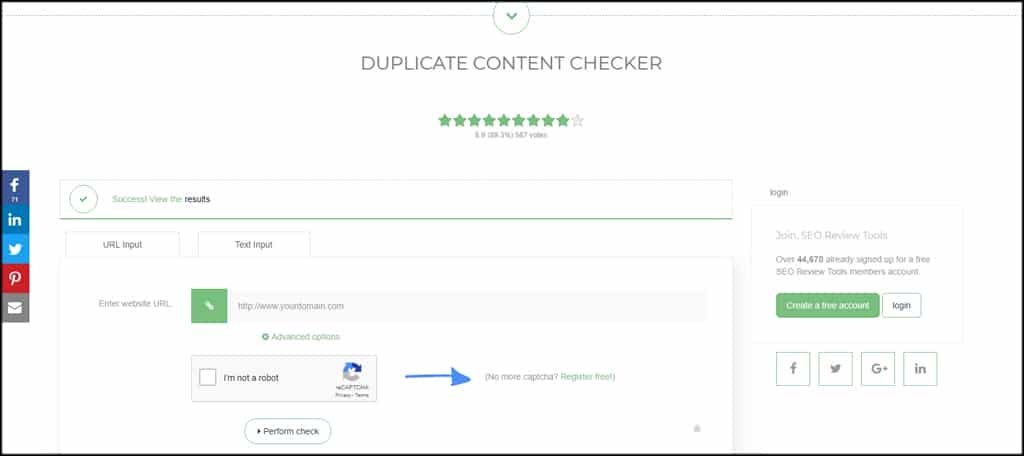
SEO Review Tools has a great platform in Duplicate Content Tracker. You can choose between URL or text input for your material. You also have a couple of advanced options for using one or two data points to match.
The system can work well as a plagiarism checker, especially if you use up to 150 words in the text search.
It checks for both external and internal copies of texts and doesn’t include things like tags and categories within content management systems like WordPress.
Using Siteliner

Siteliner is a great Google duplicate content checker tool. It’s simple to use and its free account does wonders for finding connections between external and internal text.
However, it will give you false positives, as do many other systems. For example, tags and categories of WordPress websites can trigger duplicate content warnings in the system.
Even though these elements are part of the WordPress system and don’t necessarily rank in Google.
9 Ways to Prevent Duplicate Content
Although there are many things that can cause duplicate content, you should still do what you can to avoid it. While some situations might be out of your hands, reducing copies can help your original content in terms of SEO.
And some of these methods are quite simple to implement immediately. It’s all about understanding Google duplicate content rules and how to avoid a loss in ranking because of copied materials.
1. Setting a Preferred Domain in Google

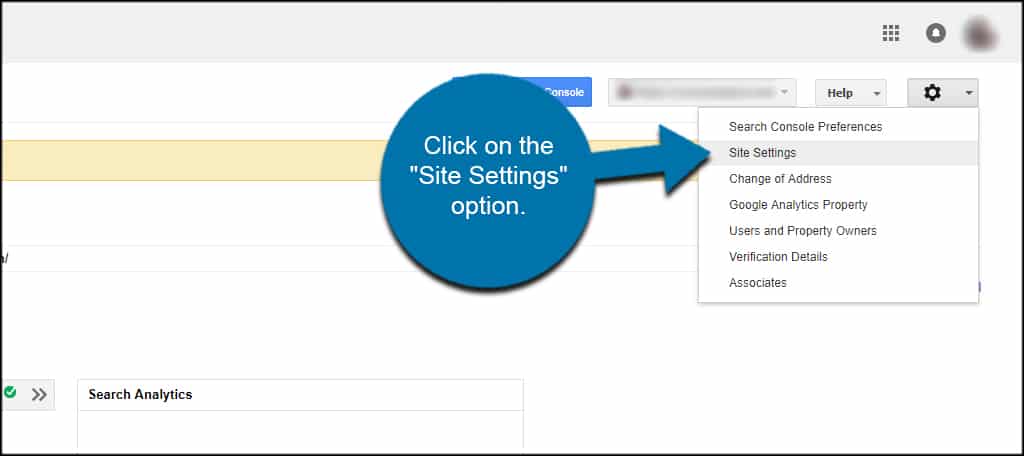
The first thing you should do is set a preferred domain in Search Console of Google. This part of the free Webmasters Tools available when you set up an account.
To access this, open the URL of your site in Search Console and click the gear icon on the top right. You want to click on the “Site Settings” option.
From here, you can choose which style is your preferred domain.
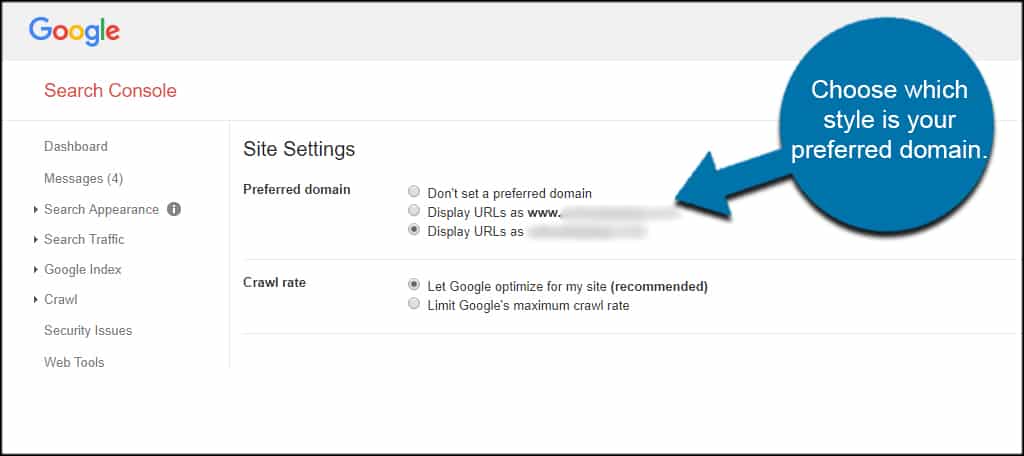
This tells Google how you want the site to appear, whether it’s using “www” or not in its URL structure.
Just make sure you follow the same layout when linking to things like posts or pictures within your website.
2. Don’t Differentiate Your Links Canonically

This goes along with what I was saying just a second ago. When linking internally, keep them all the same layout and style. This is important whether you use Search Console or not.
For instance, if you used something like, “https://www.yoursite.com/content/” don’t use a linking structure like “https://yoursite.com/content.”
In this example, the difference is both the “www” and the slash at the end.
It’s also helpful to refrain from using “http:” after setting up a website with an SSL certificate. Although the link should still work and be redirected temporarily, it’s best if you use “https:” instead.
3. Avoid Boilerplate Text when Possible

Boilerplate content is a term that means using templates for a specific content layout. For instance, many people will have a long copyright disclaimer or other pieces of content that are used on multiple pages.
However, this isn’t necessarily a bad thing in every situation. Take author bios, for example. These are often a paragraph long and usually displayed on every piece of content the writer created.
Just make sure you’re not over-using certain lines of text or phrases within the actual content.
4. Use a Print Style Sheet instead of Printer-Friendly Pages

Some developers will include a printer-friendly version of a website in case someone wants a hard copy of the content. It’s helpful in situations like contract form templates and other vital pieces of information.
Instead of adding this version, it’s better to use a print command in a style sheet of the site.
Using commands in CSS, you can control how the print comes out including image sizes, fonts, and even colors.
This saves from being duplicated and keeps the site clean and performing well.
5. Reconsider Tracking Methods for Content
![]()
In some cases, the question mark operator in the URL for tracking can lead to duplicating content. So something like this can appear as double content when search engines crawl the page:
https://yourwebsite.com/?utm_source=newsletter
Instead of the question mark, use the hashtag operator instead when creating the link. It would look like this:
https://yourwebsite.com/#utm_source=newsletter
During a crawl, search engines stop at the hashtag. Which means anything after it is ignored. This gives you a way to still track the click while only indexing the content once.
6. Redirect Duplicated Content

Duplicating content often happens when you move content to a new location or domain without creating a redirect.
For instance, what if you changed your preferred domain from “https://www.” to just “https://”? Google will then have both versions of the content indexed.
This is when you would set up a 301 redirect from the old domain layout to the new. This tells search engines and users that you are permanently moving the content from one domain layout to another – ie. your preferred domain.
7. Beware of Syndication Problems

Syndication is a great way to get your content spread across the Internet. However, it can also pose the problem of duplicating content for SEO.
An example of this is if a content curator pulls posts from your site to show on his or her pages. In many instances, these developers will offer a link back to your original article.
But when they don’t, it causes a duplication.
You may also want to consider asking the curating site owner to include a rel=”noindex” or using the rel=”tag” link functions.
8. Learn Your CMS

If you decide to use a content management system like WordPress, spend time understanding how it lays out content. For instance, some themes and plugins let you show articles on the front page.
This creates an internal duplicate if too much of the content is present.
Creating these copies can also happen in category and tag pages.
You can avoid some of these issues by only showing an excerpt of the text. In WordPress, you can add the “More” tag after the first paragraph or two. This separates a snippet of the post from the actual content.
9. Be As Unique as Possible

Perhaps the best way to avoid Google seeing duplicate content is by being as unique as possible. This goes beyond simply creating text in your article, though.
Try to use unique:
- Titles
- Tags
- Categories
- Images
The more you can differentiate your content from others, the better.
I know there isn’t much of a choice in certain things, such as creating specific categories for eCommerce, but try to be as original as you can.
Besides, this looks exceptionally good from a visitor’s perspective.
Keep Duplication from Hindering Performance
Although you won’t suffer a direct Google duplicate content penalty, it still makes it more difficult to succeed in search engine optimization. You don’t want to confuse search engines by not clearly laying out unique instances of content.
Take the time to routinely check your site. You never know if someone is scraping your content unless you check.
